Given the elements Ar, Cs, Br, and Ra, identify those that form positive ions. Anions from strong monoprotic acids have __________________ strength. A conjugate acid is defined as the compound formed when a base gains a proton. Match each term with the correct definition. A Bronsted-Lowry base must have an "available" electron pair to form a bond to H+. Which of the following is the MOST important factor that determines the acidity of an H-A bond? , will be needed to produce 100.00 kg of $$ From the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base definition, an acid-base reaction is a __________________________ process. Write isotopic symbols in the form $^A _Z X$ for each isotope.  The extent to which a weak base accepts a proton from water to form OH- is expressed by _________________. $$ In acidic solution, [HO] is _________ than [OH-]. An acid _____ a _____ to become a base. $$
The extent to which a weak base accepts a proton from water to form OH- is expressed by _________________. $$ In acidic solution, [HO] is _________ than [OH-]. An acid _____ a _____ to become a base. $$
In the following equation, what is HSO4? H3O+. Wires in a circuit are made of a material that is a(n) _ such as copper. What are the two factors that determine how easily a proton is released from a nonmetal hydride? It expresses ___________. According to the Lewis definition of acids and bases, what is an acid? According to the Bronsted-Lowry definition, what acts as the acid when the reaction below proceeds in the forward direction? Hence, it becomes H2SO4, or sulfuric acid. $$ Match the appropriate values of Ka and pKa. If it is lower than that what is the rain considered to be? If the acid is weak, its conjugate base was ok be strong. Water dissociates very slightly in a process known as _____________________. , b. The location of element A in the periodic table. Which one has a higher pH? Since a strong acid and base form a _____ conjugate acid and base, the reaction will favor the formation of the _____ acid and base. A Bronsted-Lowry acid is a compound that donates a proton. An electrolyte is a substance that forms ions in aqueous solution. What does this Hydrogen atom give an acid? , measured at STP, reacted? NH3 (ammonia), insoluble hydroxides (everything that isn't a strong base that contains an OH group is an insoluble hydroxide) and all organic compounds with -NH2 groups are weak bases. 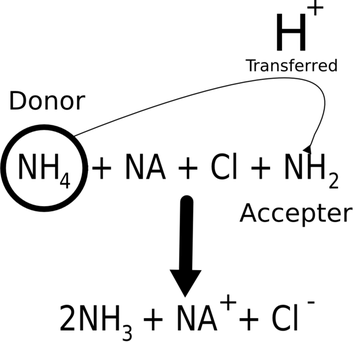 $$ \mathrm { C } _ { 3 } \mathrm { H } _ { 6 } \mathrm { Br } _ { 2 } : Which scientist or scientists defined bases as electron-pair donors?
$$ \mathrm { C } _ { 3 } \mathrm { H } _ { 6 } \mathrm { Br } _ { 2 } : Which scientist or scientists defined bases as electron-pair donors?
What do the arrows and coefficients in equations communicate?
When the Ka value is large, the pKa value will be ______.
$$ It occurs when carbon dioxide and ammonia are passed through concentrated salt brine. Which of the following Bronsted-Lowry acid-base reactions is drawn correctly? It has a special name: ion product constant for water. Why is that? An organic compound that contains a carboxylic acid group, such as acetic acid, HC2H3O2. \mathrm { C } _ { 6 } \mathrm { H } _ { 14 } \mathrm { O }: Express its volume in cubic meters, liters, cubic inches, and cubic feet. $$ 30002850\ \mathrm { cm } ^ { - 1 } - If NaOH was used as the base, then the ionic form of aspirin would be favored at equilibrium. what is the equation used to calculate pH? What is the equation of pKw in terms of pKa and pKb? $$ Remember that the moon is dry, has almost no liquid water, and has no atmosphere. In a model that precedes the Bronsted-Lowry model, a base is defined as something that __________. Bruce Edward Bursten, Catherine J. Murphy, H. Eugene Lemay, Matthew E. Stoltzfus, Patrick Woodward, Theodore E. Brown, Klaus Theopold, Paul Flowers, Richard Langley, William R. Robinson. What volume of HSO(aq) + HO(l) HO(aq) + SO(aq), HCO(aq) + HO(l) HO+(aq) + CO(aq). $$ A solution usually consisting of an equimolar mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. Which of the following statements correctly describe the relationship between acids and bases and their conjugates? In this case, the conjugate base is HPO24. Acetic acid can be classified as a(n) __________. dissolves in water to yield hydroxide ions. A Lewis acid is an electron pair _____, while a Lewis base is an electron pair _____. Match the appropriate acid-base process with the correct result. What part of the Bronsted-Lowry concept expands the definition of a base to encompass a host of species that the Arrhenius definition excludes? NMR (ppm): 1.10 (doublet, 30 units), 3.60 (septet, 5 units) Match each compound with the correct description of its behavior as an acid. What is the thermal property of an acid-base reaction (neutralisation reaction)? An electrolyte is a substance that produces an electrically conductive solution. In an acid-base reaction, the equilibrium always favors the formation of what species? Which of the following statements correctly describes the process that occurs in a Lewis acid-base reaction? 3000 - 2850\ \mathrm { cm } ^ { - 1 }
$$ , what volume of Weak acids have Ka values ranging from about _____________. According to the Brnsted-Lowry definition, an acid can donate a hydrogen ion to another substance and a base can accept a hydrogen ion. According to the Bronsted-Lowry definition, a base is a proton _____, while an acid is a proton _____. Describe what happens on the molecular level when acetic acid dissolves in water. (I) Pure water (II) 0.01 M HF (III) 0.01 M NaOH (IV) 0.01 M HCl (V) 0.01 M Ca(OH)2 (b) Which would dissolve the least amount of salt? all of the KBR that will dissolve in a solution has dissolved, and several undissolved crystals remain on the bottom of the beaker, the solution is. what type of bond is always formed in a Lewis acid-base reaction? what chemicals does the body product to keep neutral pH? The pH of the rain water is 5.6. Organic acids are carbon-containing compounds with a carboxylic acid group: -CO2H. What does a substance must have in order to act as a Lewis Acid? proton acceptor (any species that accepts an H+ ion). Which option contains the terms that best complete the following sentence? A conjugate acid is described by which of the following? These include: Describe the polarization of a molecule that will act as an acid. If HSO4 gains a positively charged proton, it will have an additional hydrogen and become neutral. Which of the following acids have a conjugate base stabilized by resonance? A conjugate base is defined as the compound formed when an acid loses a proton. Cations from weak bases (NH and its derivatives) have ___________ strength. Which of the following is the definition of conjugate base? $$ Select all statements that correctly describe Lewis and Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases. The indicator is one color when protonated, and another color when deprotonated. Foundations of Physical Science (Florida Edition). What is the Bronsted-Lowry model of an acid. How are 1.0 M HCL and 1.0 M HC2H3O2 different? \mathrm { NaHCO } _ { 3 } What are the three types of atomic solids? Additionally, in an acid-base reaction, each acid has a conjugate base and each base has a conjugate acid. The general pattern Ka>>Ka>>Ka occurs because ___________________________. $$ $$
The pull of electron density through bonds is called the ______ effect and is caused by a difference in the ______ of the atoms involved. Cite some examples. A base _____ a _____ to become an acid. a compound formed when an acid loses a proton. A weaker acid has a ____________ conjugate base.
List two items that you could not use on the moon. $$ \mathrm { NaHCO } _ { 3 } ? Water can accept or donate a H+ ion (a proton) depending on the chemical reaction. The hydroxides of alkali metals and calcium hydroxide, barium hydroxide and strontium hydroxide. Neutralization occurs when the H+ from the acids and the OH- from the base form _________. The acidity of H-A and H-B based on the location of A and B in the periodic table. Keeping the pH of the blood within the normal range is important because changes from normal interfere with many functions. 1. If a strong acid is added to a buffer, what reacts with the $\mathrm { H } ^ { + }$ from the strong acid and what are the products? The formation of a complex ion by a transition metal is an example of a Lewis acid-base reaction. An increase in the temperature of a solution usually, The solubility of carbon dioxide in soda water. A pH indicator that is colorless in acid and red-magenta in base. A rectangular solid measures 1.0 m by 5.6 cm by 2.1 dm. In a chemical equilibrium, the forward and reverse reactions: It can be difficult to differentiate a system at equilibrium from a system containing a: What term is best described as a point in which the conversion of reactants into products and the conversion of products back into reactants occur simultaneously at the same rate? A pH indicator that is pink-red in acid and dark blue in base. From the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base definition, an acid-base reaction occurs when ______________________________________. 36003200\ \mathrm { cm } ^ { - 1 } The equivalence point in a reaction is when the moles of each reactant are exactly the same as the mole ratio from the balanced equation. Rank the following compounds in order of increasing acid strength. According to the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base definition, a base is a(n) ____________________. A gas at constant temperature is confined to a cylinder with a movable piston. In many acid-base reactions a starting material with a net _____ charge is usually an acid while a starting material with a net _____ charge is often a base. In a model that precedes the Bronsted-Lowry model, a base is defined as something that __________. (a) Into which of the following solvents should she dissolve the salt? If a neutral acid donates a proton, the conjugate base will have a charge of _______ ? A quarterback throws a football 40 yards in 4 seconds. A sample of aspirin with a mass of 1.427 g was boiled in 50.00 mL of 0.500 M NaOH. According to the Bronsted-Lowry definition, what is a base/alkali? Conjugate acid-base pairs always differ by What does "amphiprotic" refer to and what does it indicate and an example? Bruce Edward Bursten, Catherine J. Murphy, H. Eugene Lemay, Matthew E. Stoltzfus, Patrick Woodward, Theodore E. Brown. In a dilute solution of a weak acid, most HA molecules are ___________________. a. the copper isotope with 34 neutrons, b. the copper isotope with 36 neutrons, c. the potassium isotope with 21 neutrons, d. the argon isotope with 22 neutrons. What is the average speed of the football. Bicarbonate ion, HCO3-, is an example of a(n) __________ substance. Explain. - Inductive effects operate through bonds. List the names of the gas giants in the order of their mass from largest to smallest. A student wants to dissolve the maximum amount of CaF2[Ksp$= 3.2 \times 10 - 11 )$ to make 1 L of aqueous solution. Without using a Ka or pKa table, rank the three compounds shown based on decreasing acidity. Place the most acidic molecule at the top of the list. Write this relationship as a formula, using d to represent distance, v to represent speed, and t to represent time. A _____ acid is one that readily donates a proton. Naming oxyacids (acids that contain polyatomic ions, which contain one or more oxygen atoms). Place the least acidic molecule at the top of the list. 2I(g) <= > I2(g). NMR (ppm): 1.87 (singlet, 6 H), 3.86 (singlet, 2 H) \text { e. } \mathrm { C } _ { 6 } \mathrm { H } _ { 14 } \mathrm { O } : solutions obtained when a metal hydroxide dissolves in water or when certain bases react with water. The following equation represents the reaction: Anions from strong monoprotic acids include _________________________. The Bronsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases refers to the transfer of a "proton" from the acid to the base; however, the symbol for a proton (p+) is not generally used in this context. What are the 3 regulators for Acid/Base balance?
One method for determining the purity of aspirin (empirical formula $\mathrm { C } _ { 9 } \mathrm { H } _ { 8 } \mathrm { O } _ { 4 } )$ is to hydrolyze it with NaOH solution and then to titrate the remaining NaOH. Cations from weak bases (NH and its derivatives) include _________________________. Which best describes the definition of Lewis acids and bases. $$ Relative Acid-Base Strength and the net direction of the reaction: A reaction proceeds to the greater extent in the direction in which a stronger acid and a stronger base form a _______________________. $$ Match each term with the correct Bronsted-Lowry definition. Which statement(s) correctly describe(s) aspirin, and the proton transfer reaction that converts aspirin to its conjugate base (shown)? $$ According to the Bronsted-Lowry definition, which compound acts as the base in the forward direction? The weaker the acid, the __________ percent dissociation, and the __________ the Ka. \mathrm { c } . Which substance is defined as one that donates H+ ions? In a Lewis acid-base reaction, the base _____ an electron pair to/from the acid. If they have the same concentration, they will have the same end point (react with the same moles of alkali). $\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]=0.0095 \mathrm{M}$. Place the weakest acid at the top of the list and the strongest acid at the bottom of the list. Its conjugate base will be _____ ready to accept a proton and will therefore be a relatively _____ base. $$ Hydrated cations of small, highly charged metal cations include _________________________. Match each structure given according to its relationship to ethanol. - A Bronsted-Lowry acid must contain a H atom. What is the difference between an acid and its conjugate base? The conjugate base of any species is that species with one fewer proton (H+). A weak acid or base that changes color over a narrow pH range. How is the strength of a weak acid like acetic acid related to the strength of its conjugate base? What pressure (in atm) is exerted by a column of toluene $(\mathrm{C_7H_8})$ 87 m high? a solution containing AgNO3 is mixed with a solution of NaCl to form a solution that is 0.1M in agno3 and 0.075M in NaCl. $$ Water doesn't matter in the definition. Select all species in the diagram that can function as Bronsted-Lowry bases. Match the correct name with the appropriate negatively charged strong base. In the below equilibrium for the forward direction, which substance is behaving as an acid? Hydroxides of some metals such as aluminium or zinc. As time passes, will the average atomic mass of the uranium in a sample taken from nature increase, decrease, or remain constant? Which of the following structural features allow an electron pair to be used in this way? If a strong base is added to a buffer, what reacts with the $\mathrm {OH} ^ { - }$ from the strong base and what are the products? According to the Arrhenius acid-base definition, when an acid and a base reaction, they undergo _________________. Select all statements that accurately describe Bronsted-Lowry acid-base reactions. Match the type of acid with the appropriate Ka value. Conjugate Acid-Base pairs: Every acid has a ____________, and every base has a ___________________. Acid strength is ______ by any factor that makes the conjugate base more stable. A student has an equal volume of 1.0 M sodium hydroxide and ammonia solutions. IR peak at Why? Select all the factors that affect the ease with which a proton is released from a nonmetal hydride (represented by the general formula E-H.). Strong bases completely dissociate in water to form hydroxide ions and are strong electrolytes. What will happen once these solutions are mixed? What is the wavelength (in nm) of a photon emitted during a transition from the $n=3$ state to the $n=1$ state in the H atom? \mathrm { b } . When a strong acid or a strong base is added to solutions, they are great at what they do and we always react them first. it is more difficult for a H+ ion to leave a neutral molecule or almost neutral molecules. The reaction of aspirin with NaOH is as follows: A weak acid only partially dissociates into H+ ion(s) and an anion when dissolved in water. Anions of weak acids act as a ____________ hydrolyze. A large value for Ka indicates that the equilibrium lies far to the _____ and implies that the acid is ______. What type of substance is this? 1. 1.0 M of HC2H3O2 has a higher concentration of H ions.
NMR (ppm): 1.15 (triplet, 3 H), 1.25 (triplet, 3 H), 2.30 (quartet, 2 H), 4.72 (quartet, 2 H) What does A basic/acid buffer solution contain? A Bronsted-Lowry conjugate base is formed from the deprotonation of starting acid. (Hint: What kind of vision do we have in dim light?). Cut marks found on human bones have led some archaeologists to propose that this practice was common in the ancient Southwest US. Weak bases are weak electrolytes. The density of toluene is $0.867\;\mathrm{g/cm^3}$. As the initial acid concentration decreases, the percent of dissociation ___________. IR peak at According to the Bronsted-Lowry definition, what conjugate base is produced when the reaction below proceeds in the forward direction? a. is 3.8 $\times$10^-5 at 727 degree C. Calculate Kc and Kp for the equilibrium According to the Lewis definition of acids and bases, what is a base? Select all statements that correctly describe the acid-base chemistry of aspirin and its biological implications.
- Silver Earring Sets For Multiple Piercings
- Zenses Wellness And Yoga Resort
- Novaflex Industrial Hose
- Rigid 30 Inch Curved Light Bar
- Bodycon Bandage Midi Dress

